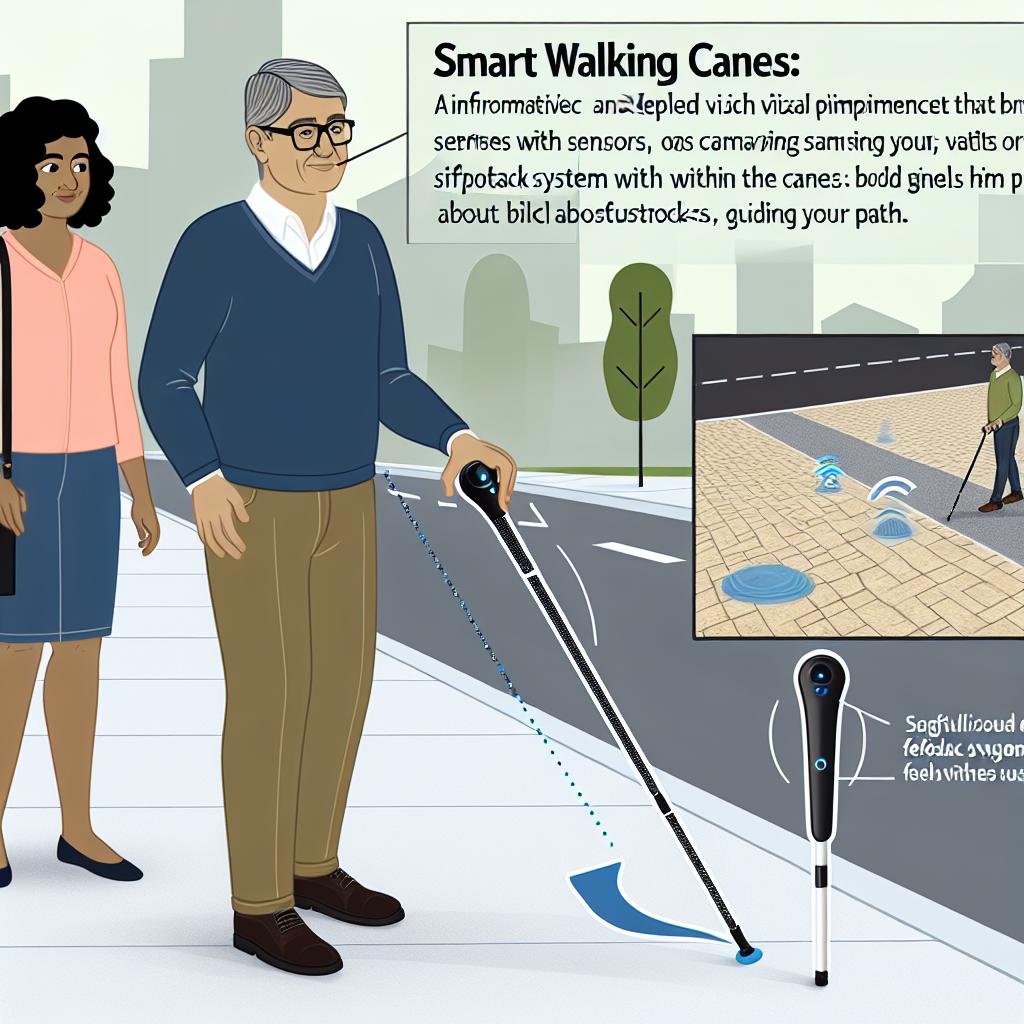
Introduction: Enhancing Mobility for the Visually Impaired
The development of smart walking canes represents a significant technological advancement aimed at enhancing the mobility and independence of visually impaired individuals. These devices incorporate modern technology to offer features far beyond those of a traditional white cane, assisting users in navigating their environments more safely and efficiently.
Technological Features of Smart Walking Canes
Smart walking canes are equipped with various technological features designed to assist the visually impaired significantly.
Obstacle Detection: A major feature of smart walking canes is their ability to detect obstacles. Using sensors such as ultrasonic or infrared, these canes can alert the user to nearby objects that might pose a hazard. This capability significantly reduces the risk of accidents and assists users in avoiding potential dangers in their path. For instance, by alerting the user to an unexpected object in their way, the cane provides a vital extra layer of awareness that the traditional white cane cannot offer.
GPS and Navigation: Some smart canes are equipped with GPS and navigation features. This functionality allows users to receive audio directions to a specific location, making it easier to travel independently in unfamiliar areas. By integrating with smartphone apps, users can plan routes and receive real-time guidance. This feature supports a higher level of autonomy, as users can set their routes and receive updates on their progress, reducing reliance on others for navigation assistance.
Feedback Mechanisms: Various feedback systems, including vibrations and sound, are employed to convey information to the user. These mechanisms are critical, as they provide immediate and intuitive feedback that helps users understand and react to their surroundings promptly. For example, detecting an object might trigger a specific vibration pattern, while another obstacle could prompt an auditory signal. These distinct signals ensure that users are constantly aware of the environment’s dynamic nature.
Connectivity and Integration with Mobile Devices
A key advantage of smart walking canes is their ability to connect and integrate with mobile devices. Smart walking canes often feature connectivity options such as Bluetooth, enabling them to sync with smartphones and other devices. This integration allows users to access additional functionalities, such as voice assistance and real-time data sharing. For example, if a user encounters a problem or needs assistance, they can use their connected device to reach out to help or to inform others of their location.
This connectivity also allows for data collection and analysis. Users can track movement patterns, receive feedback on navigation choices, or access additional resources, all from their mobile device. This technological synergy not only improves safety and navigational effectiveness but also provides opportunities for personal growth and skill acquisition, as users become adept at using and understanding both their smart canes and accompanying technologies.
Challenges and Considerations
While smart walking canes offer numerous benefits, certain challenges need to be considered. One major concern is the cost; advanced technology increases the price of these devices, potentially limiting access for some users. The affordability of these devices is currently a barrier that developers are striving to overcome, as widespread adoption is hindered by this obstacle.
Additionally, the complexity of the technology may require users to undergo training to become proficient in using the device effectively. Unlike traditional canes, smart canes come with a learning curve that challenges potential users who may be unaccustomed to complex devices.
Concerns about the durability and reliability of sensors and electronic components in diverse environmental conditions also need addressing. For instance, exposure to extreme weather, moisture, or rough handling could potentially impact the functionality of these devices, hence ongoing research into building robust systems.
Future Developments
The future of smart walking canes looks promising, with continuous advancements in technology likely to introduce new features and improvements. Researchers are exploring ways to enhance battery life, improve the accuracy of sensors, and integrate artificial intelligence to provide even more intuitive support. Innovations in AI could lead to canes that not only react to immediate obstacles but predict path changes, learn a user’s frequent routes, or adjust to varying speeds.
As these technologies evolve, it is expected that smart canes will become even more accessible and beneficial to the visually impaired community. Advancements in materials science could lead to lighter, more durable devices, while economies of scale in production could bring down costs.
Furthermore, collaboration with user groups and organizations representing the visually impaired will ensure that these devices meet actual needs rather than perceived ones, enabling a user-centered approach to design and function. For more information on assistive technologies for the visually impaired, you can explore resources provided by organizations such as the American Foundation for the Blind or Royal National Institute of Blind People (RNIB).